Thuja occidentalis
White cedar description:
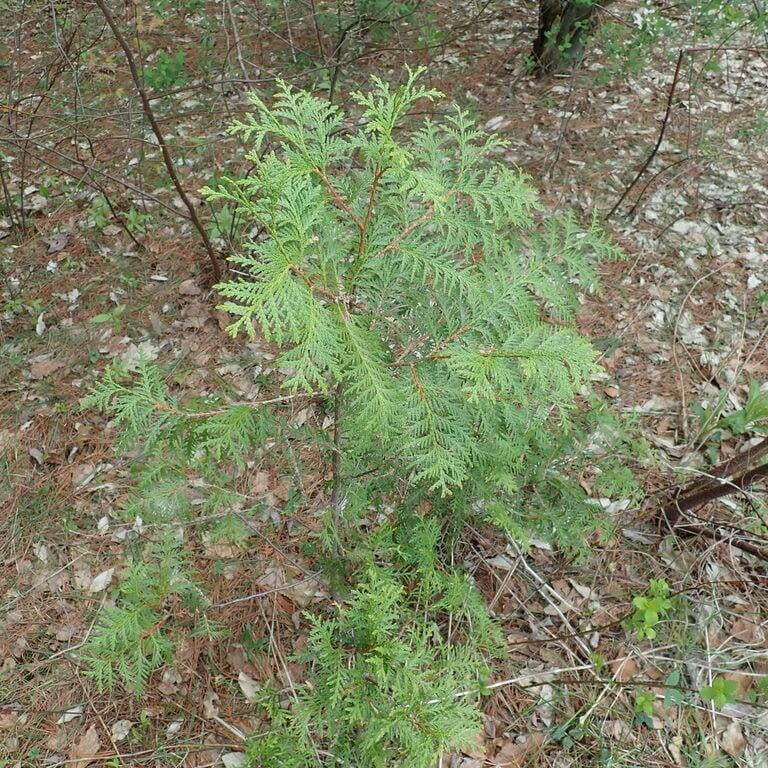
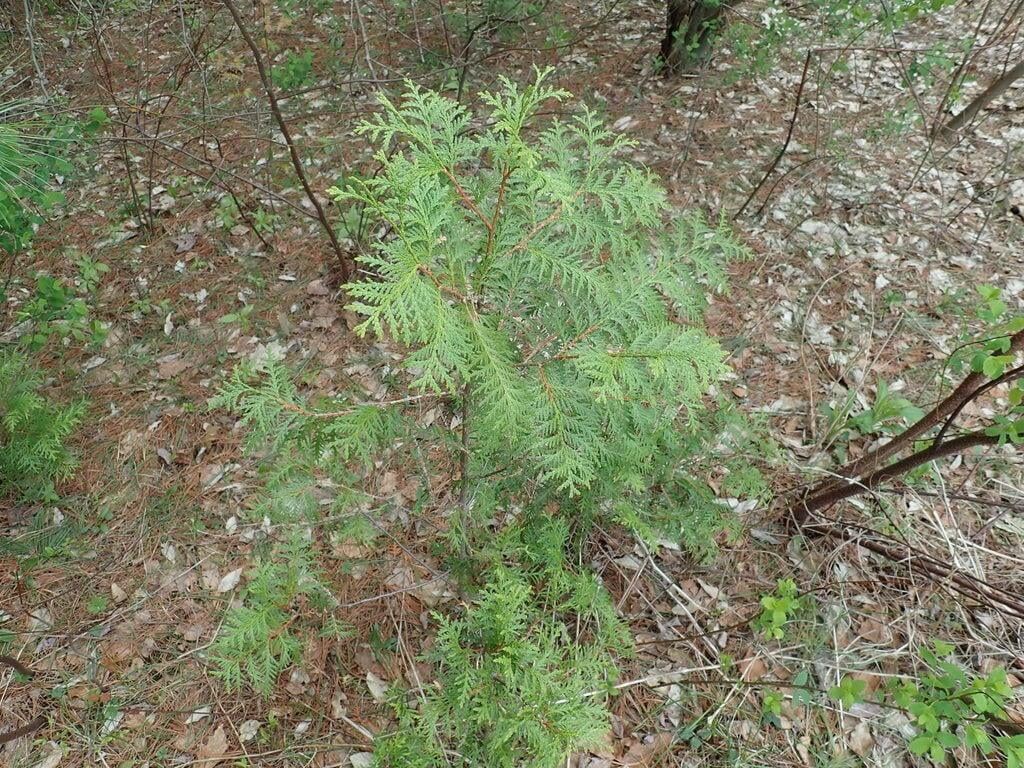
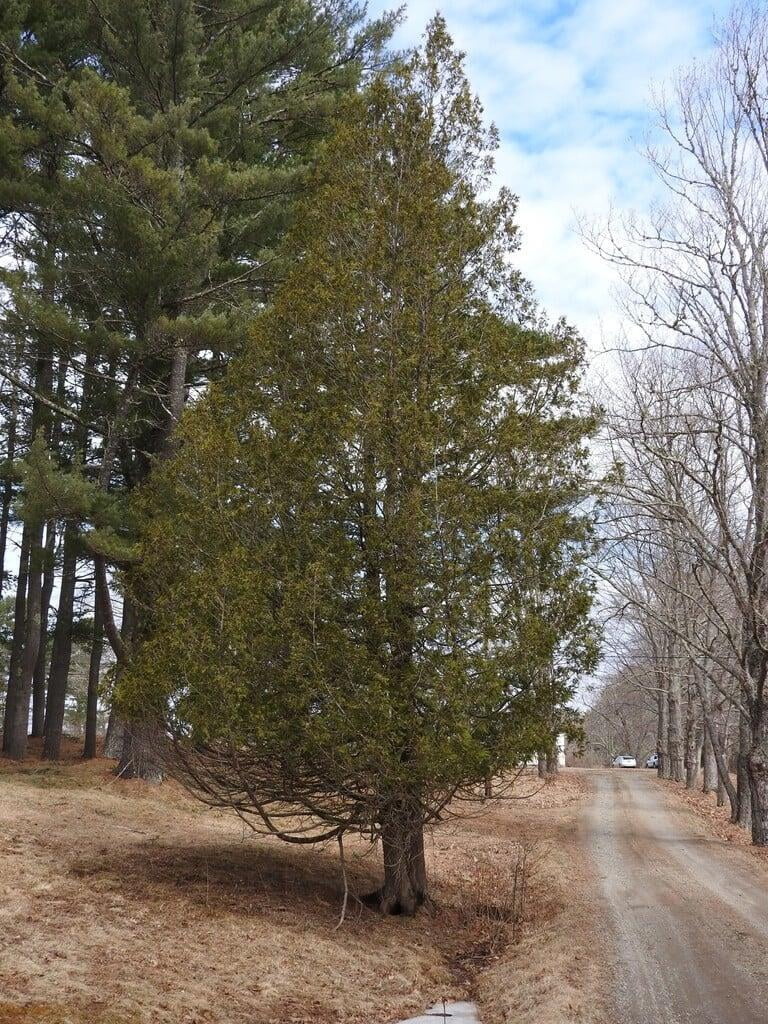
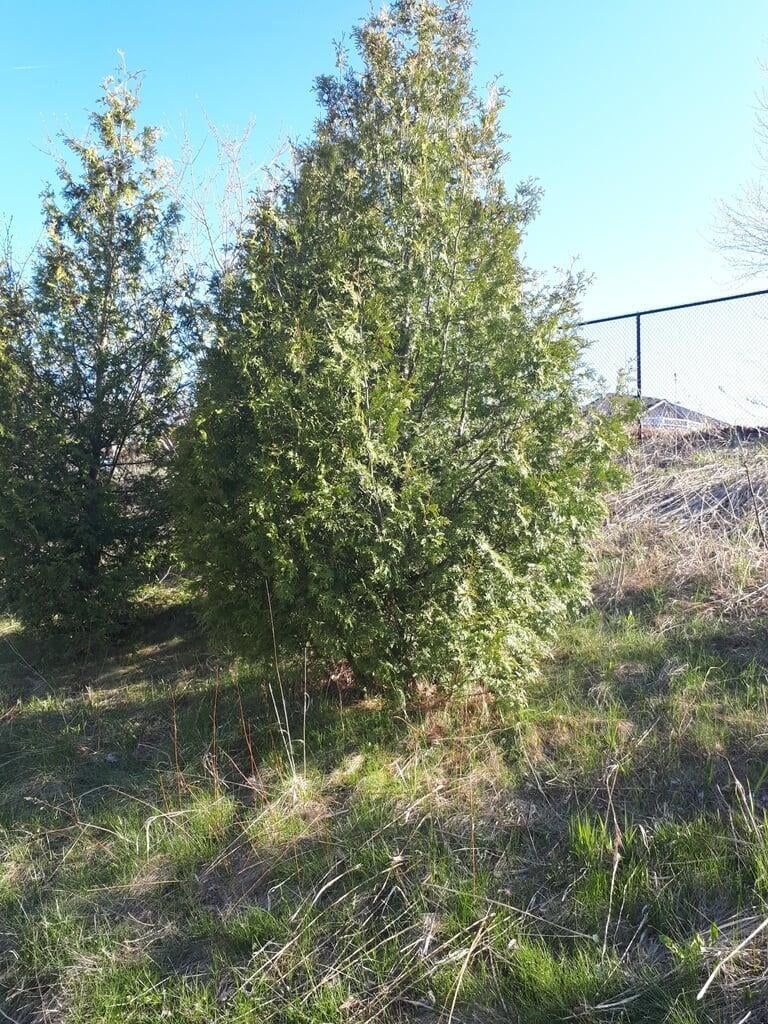
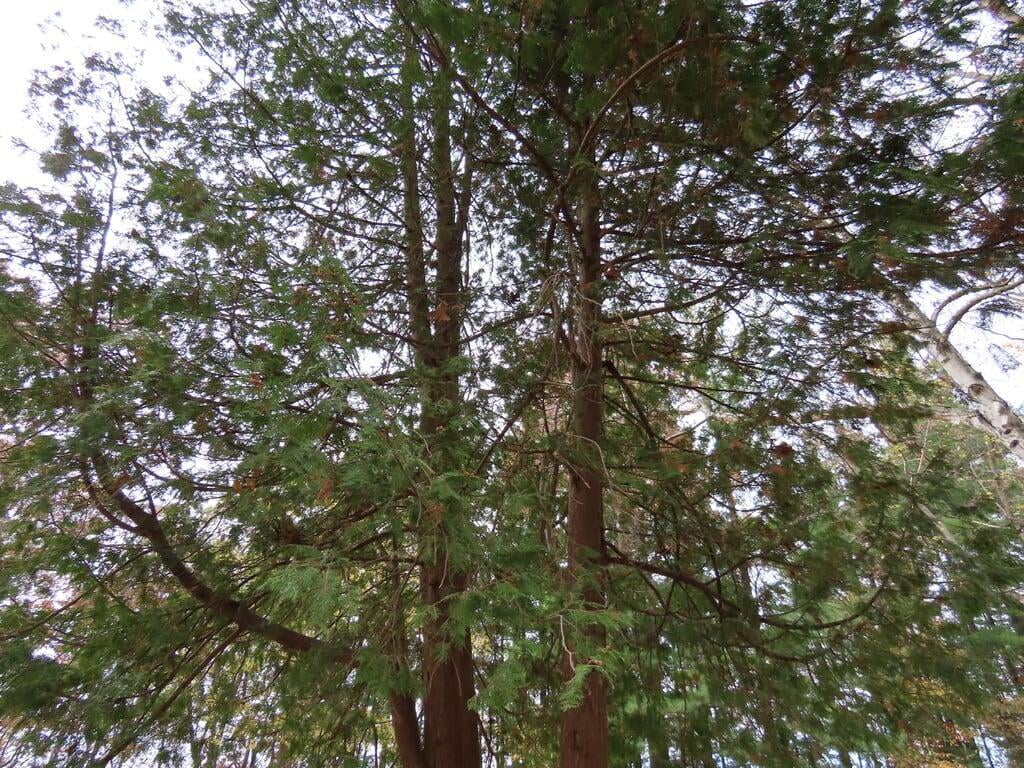
Thuja occidentalis, commonly known as Eastern arborvitae or Northern white cedar, is a coniferous evergreen tree that is native to eastern North America. The tree can grow up to a height of 40 to 80 feet and has a spread of 10 to 15 feet, making it a popular choice for hedges, screens, and privacy fences. Its slender, pyramidal shape and rich green foliage make it a visually appealing addition to any landscape.
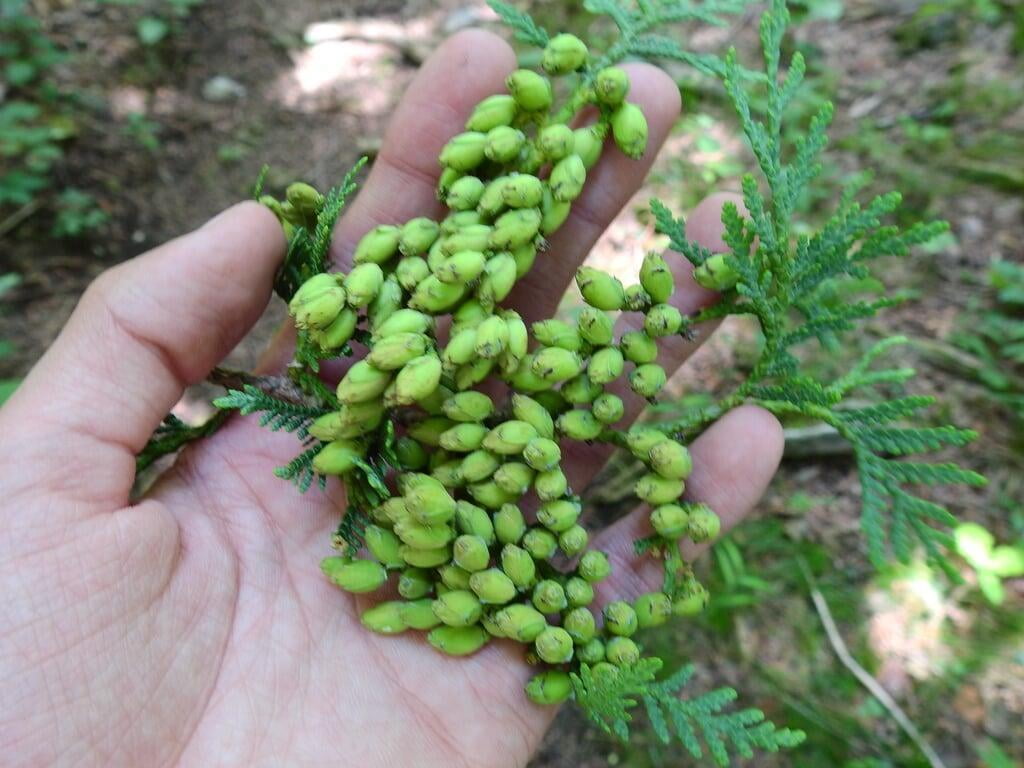
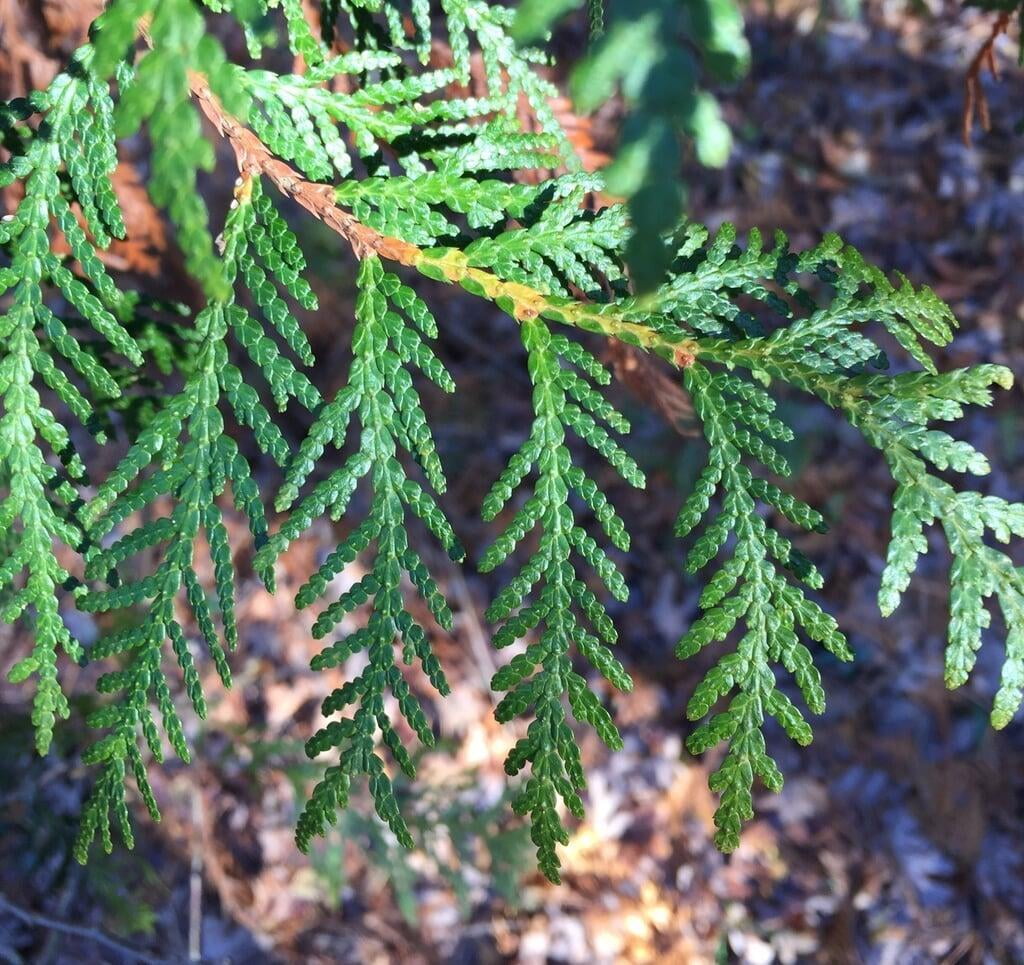
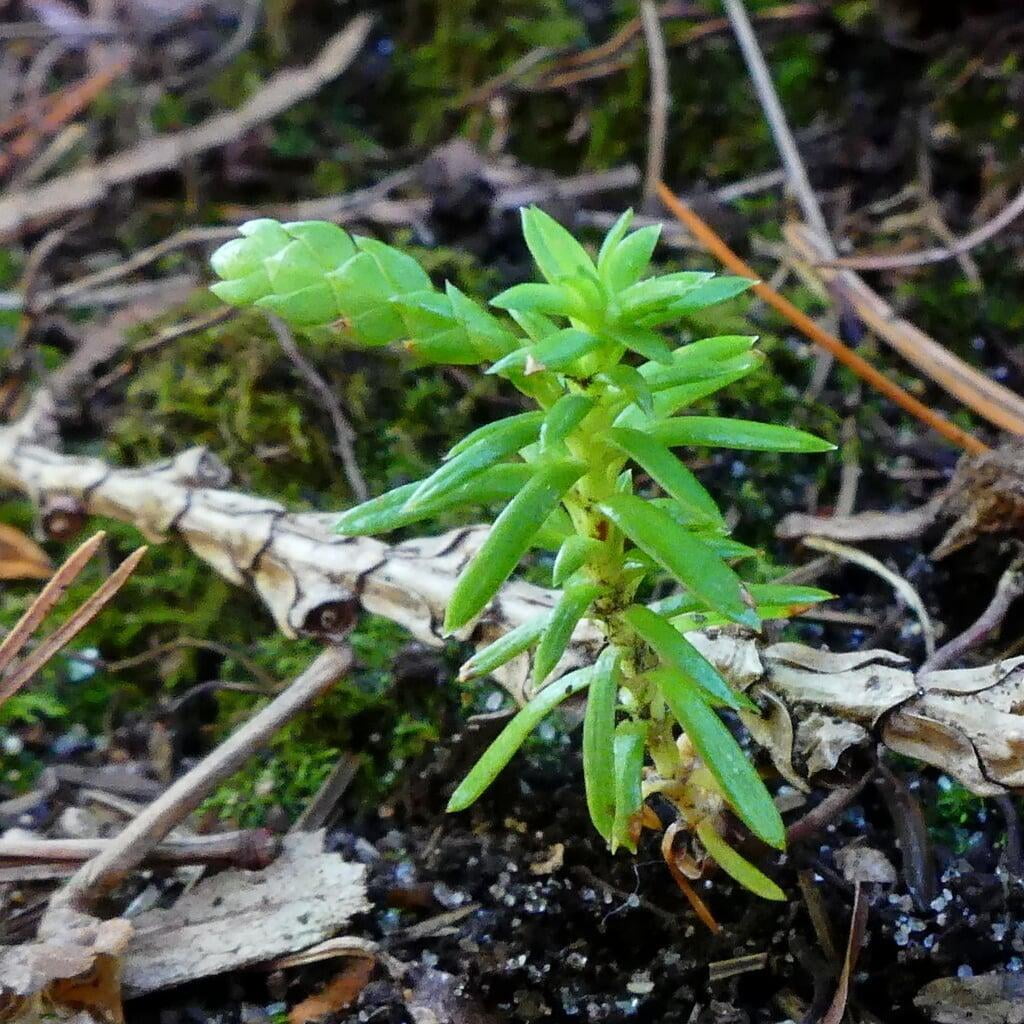
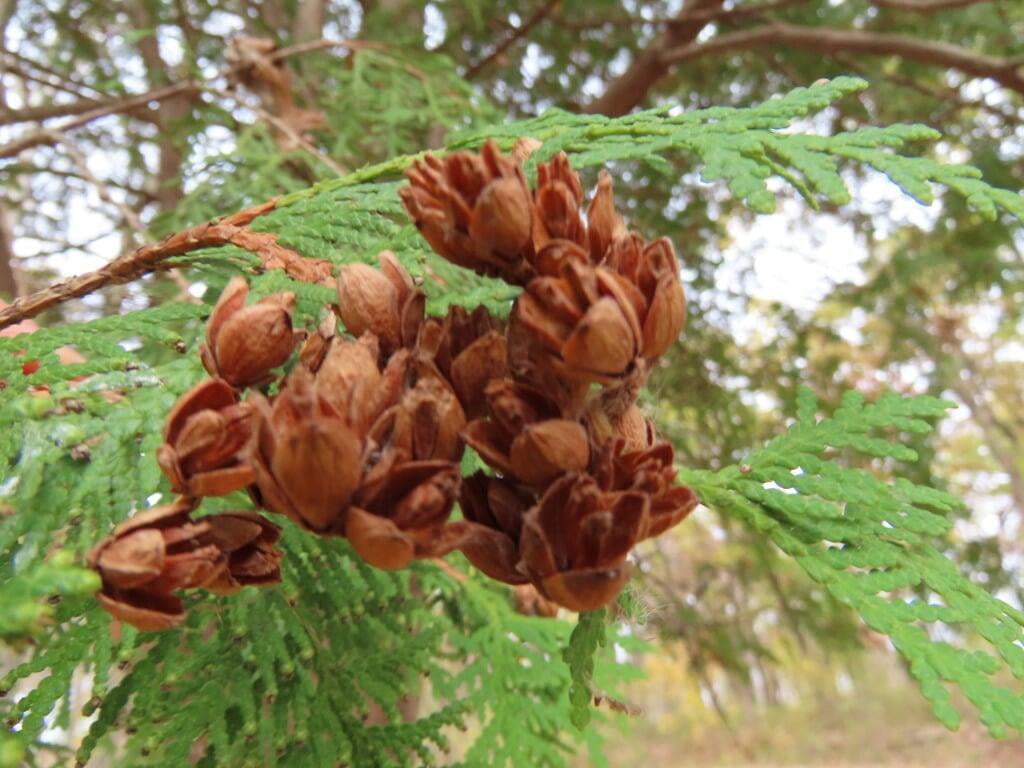
The tree's leaves are scale-like and arranged in flat sprays, with each spray measuring around 1/16 to 1/8 inch in length. The cones of Thuja occidentalis are small, measuring around 1/2 to 3/4 inch in length, and are initially green in color, turning brown as they mature. The tree also produces small, woody seed pods that measure around 1/4 inch in length.
Thuja occidentalis is widely used in traditional herbal medicine and homeopathy, with a range of potential health benefits. Its extracts are believed to have immune-boosting properties, and may help to alleviate symptoms of respiratory infections, colds, and flu. Thuja occidentalis is also used topically for skin conditions such as warts, ringworm, and psoriasis, as well as a natural insect repellent. However, it is important to note that Thuja occidentalis can be toxic in high doses, and should only be used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider.
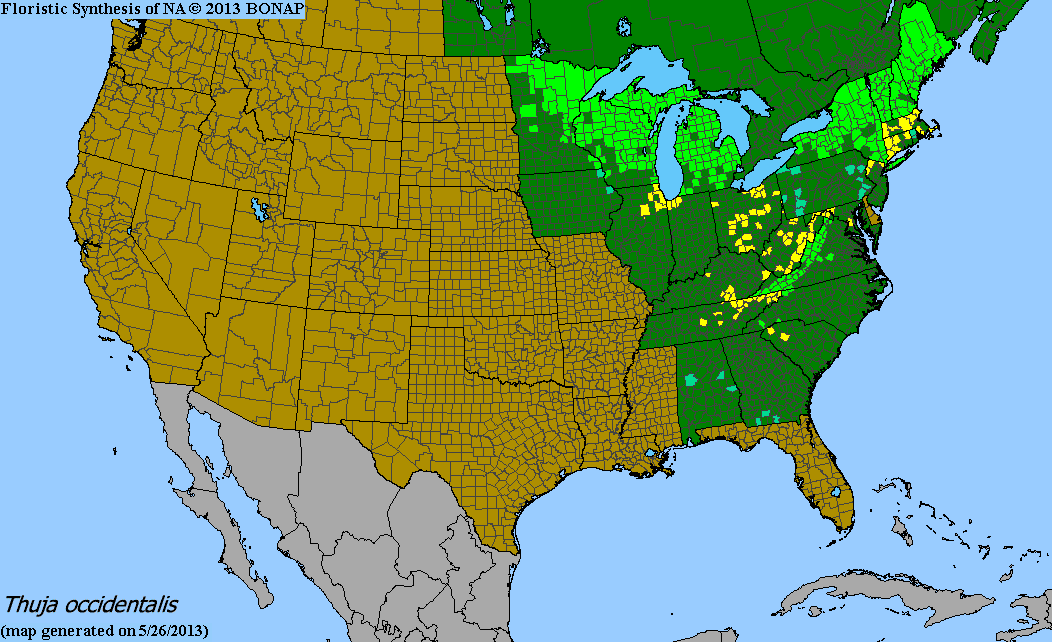
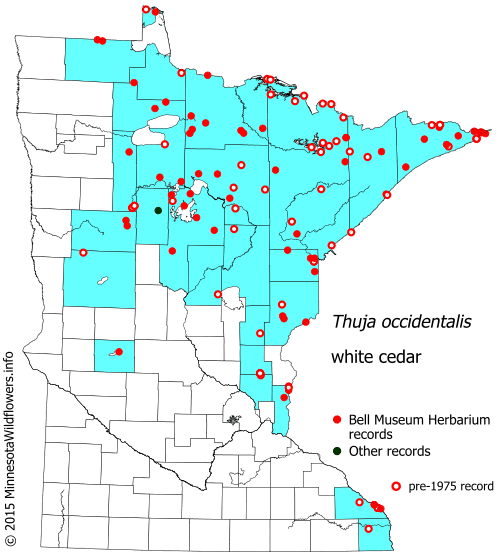
Native Range:
White cedar has a native range in the United States that extends from Minnesota on the West East and South to Maine and Georgia.
Standard Plant Information:
Plant Height: 40-80'
Bloom time: April - May
Preferred Habitat: Does well in part shade to full sun with moist to wet soil. Often found in peat swamps, moist upland forests, rocky lakeshores, and cliffs.
Planting:
Planting a tree seedling or small potted tree properly is important to ensure its healthy growth and development. Here are the steps you can follow to plant a tree:
Choose the right spot: Select a spot with adequate sunlight, water, and soil drainage. Make sure the tree has enough space to grow to its full size without interfering with other plants, structures, or utility lines.
Prepare the soil: Dig a hole that is twice as wide and slightly shallower than the root ball of the seedling. Remove weeds or debris from the area. Loosen the soil around the edges of the hole to help the roots grow more easily.
Plant the seedling: Place the seedling in the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with the ground surface. Gently spread out the roots and fill in the hole with soil, tamping it down lightly as you go.
Water the seedling: Water the tree deeply and thoroughly after planting, making sure the soil is evenly moist. This will help settle the soil around the roots and eliminate any air pockets.
Monitor the growth: Keep an eye on the seedling to make sure it is getting enough water and sunlight, and that it is not being attacked by pests or diseases. Prune any damaged or dead branches as necessary, and provide support if needed.
By following these steps, you can help ensure the healthy growth and development of your newly planted tree seedling.