Betula papyrifera
Paper birch description:
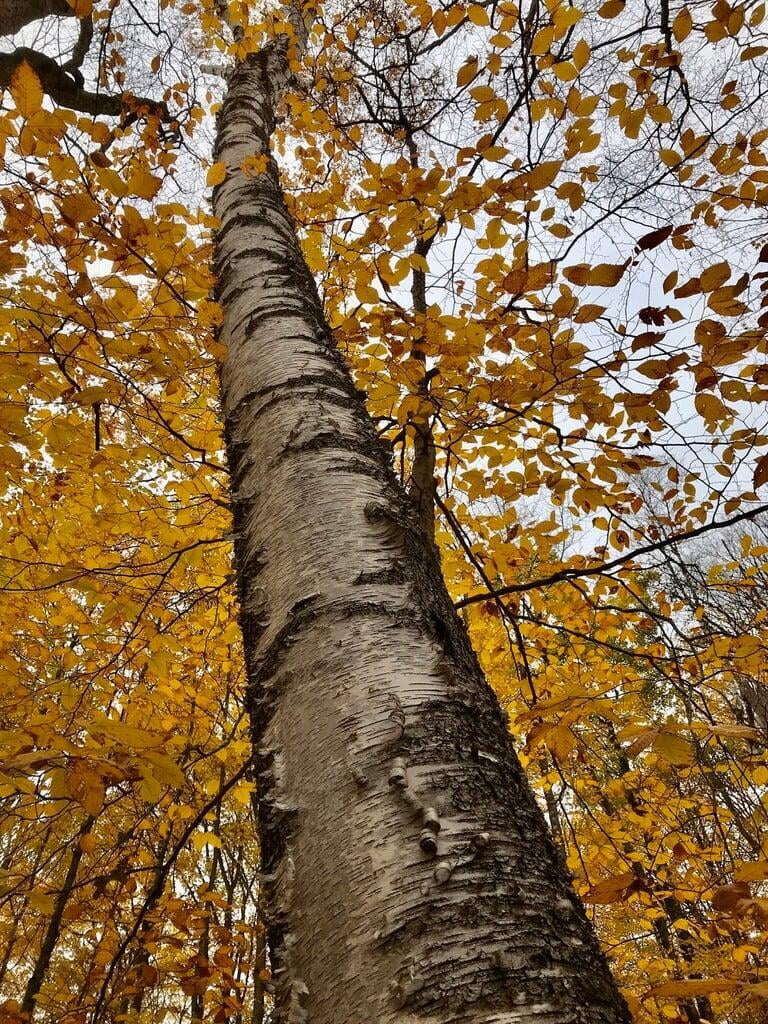
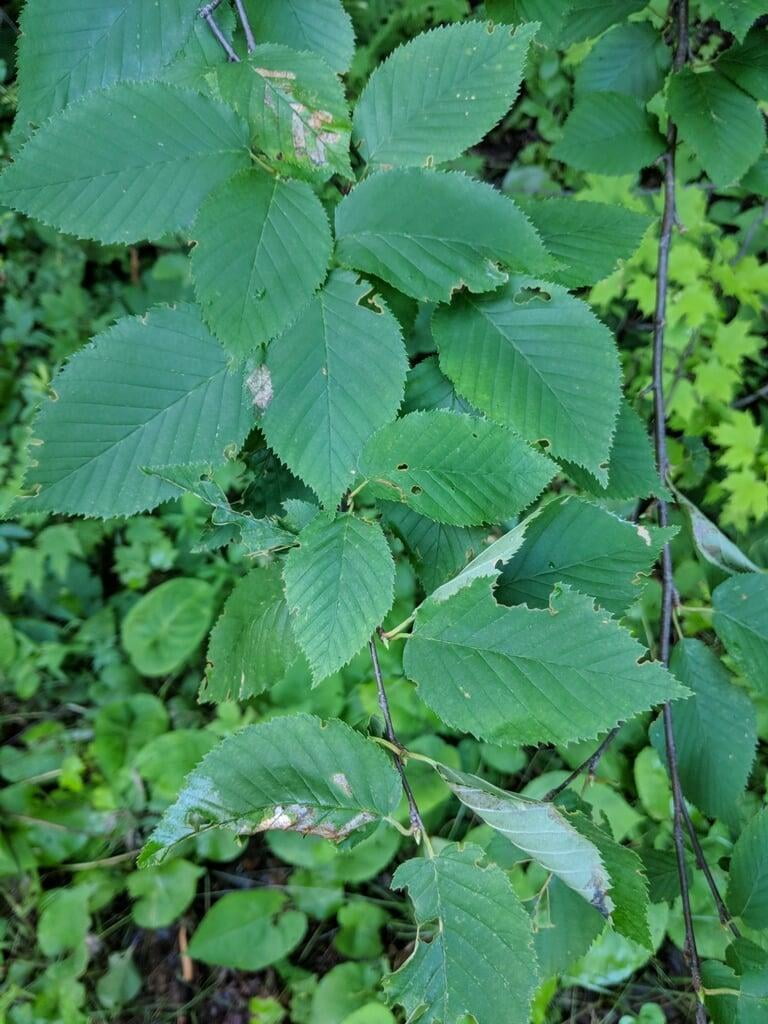
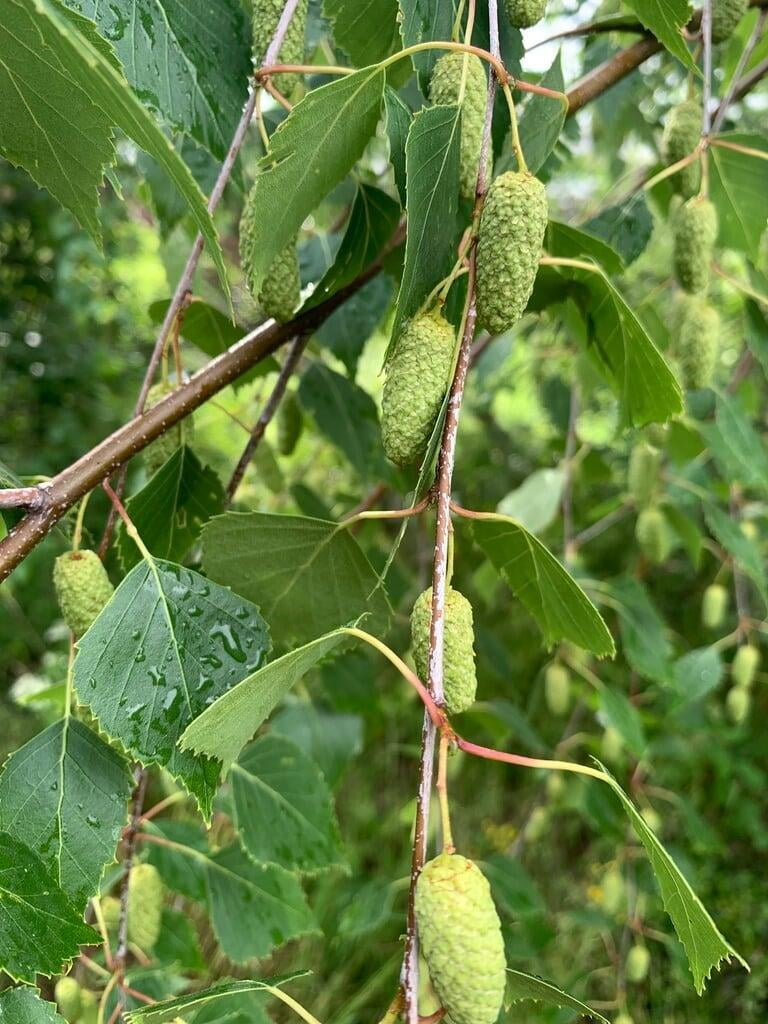
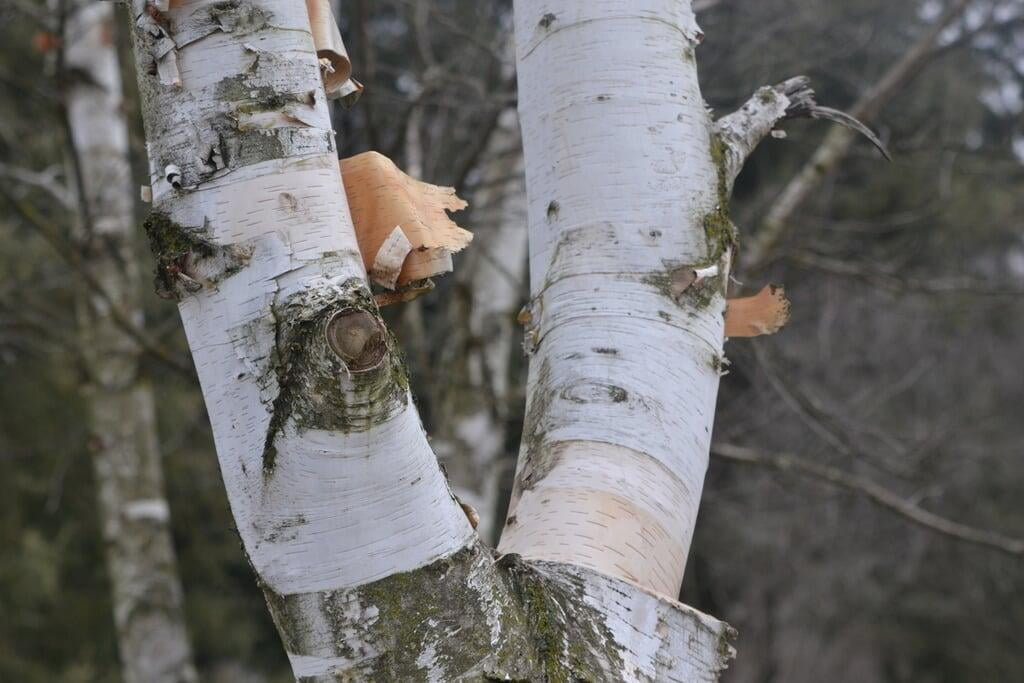
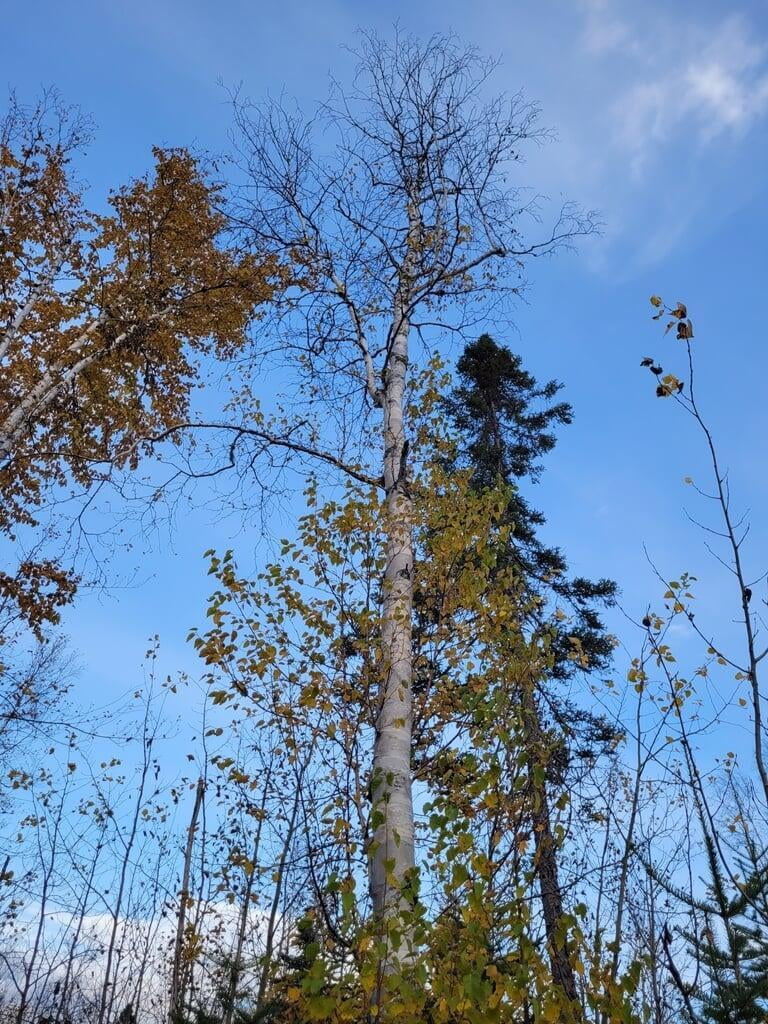
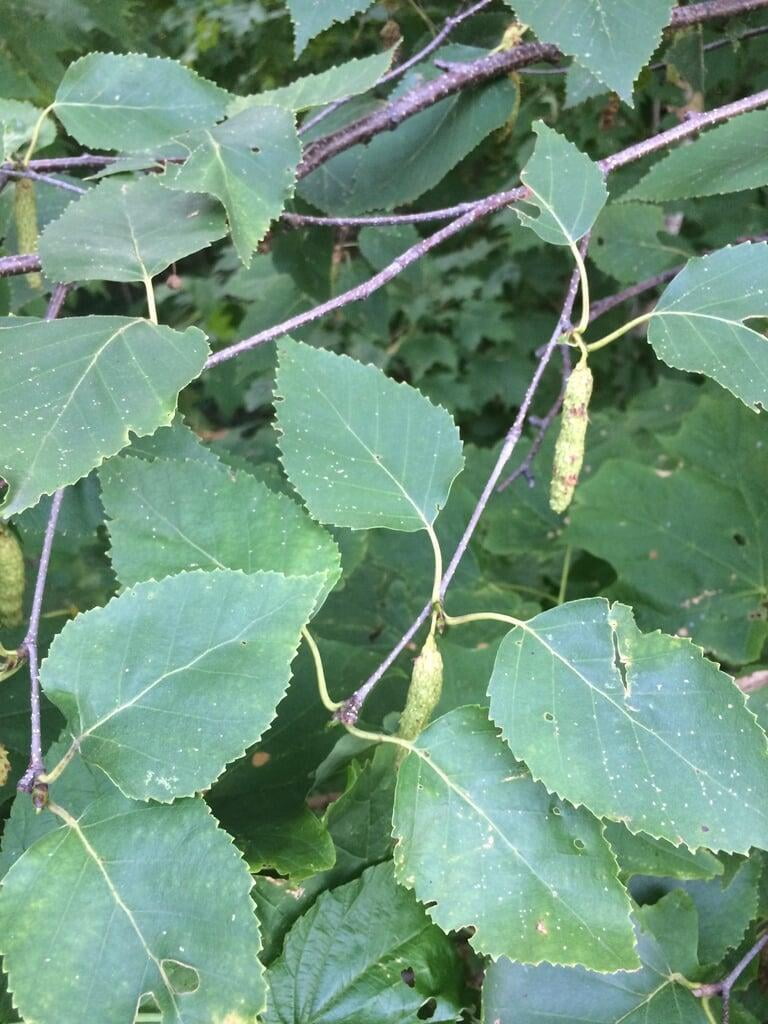
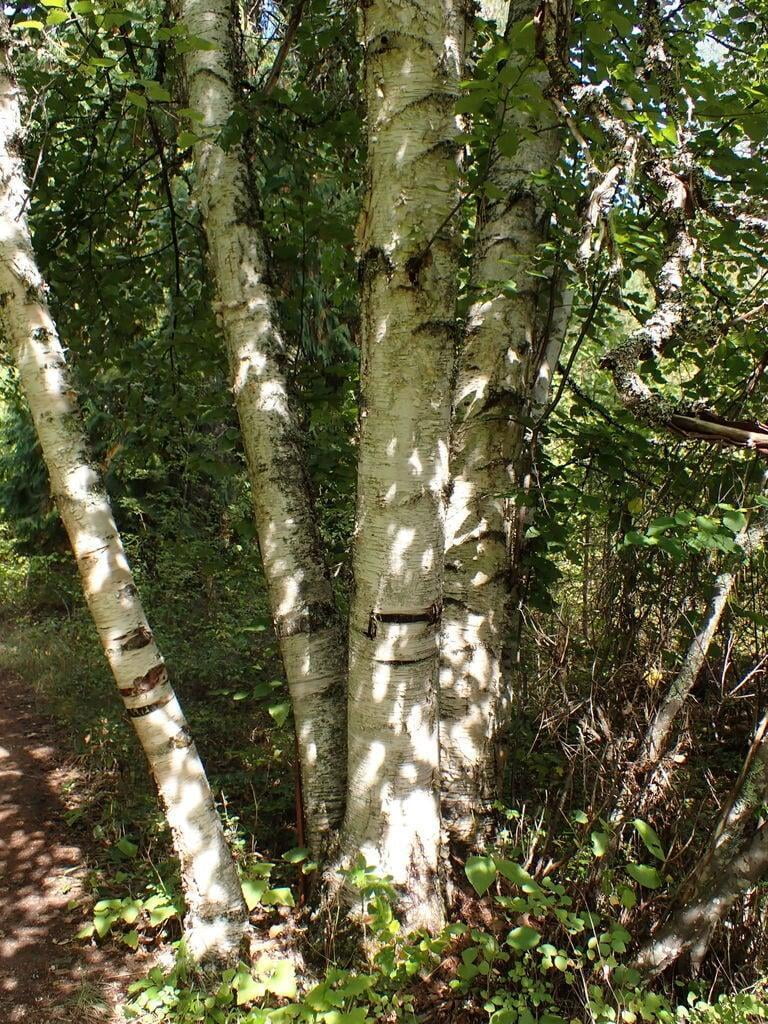
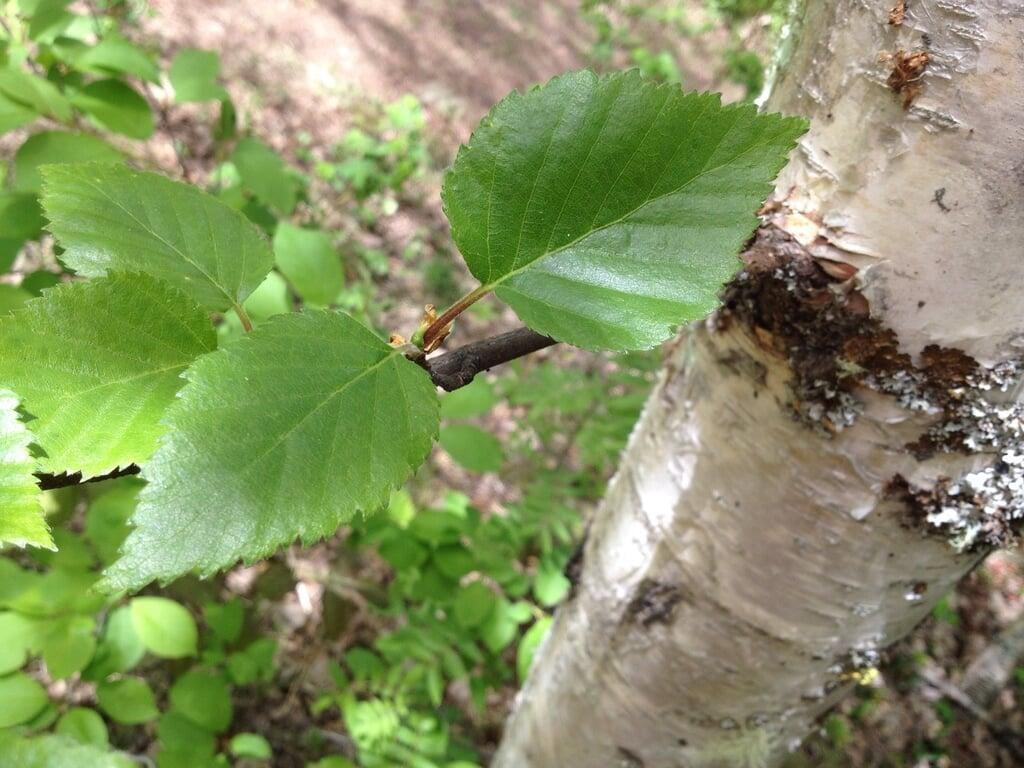
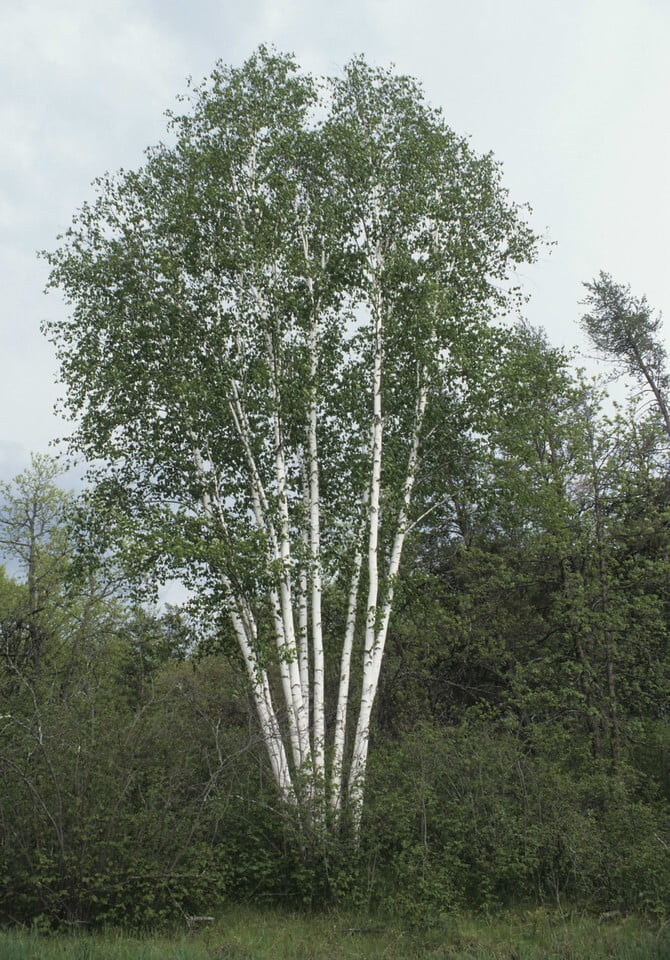
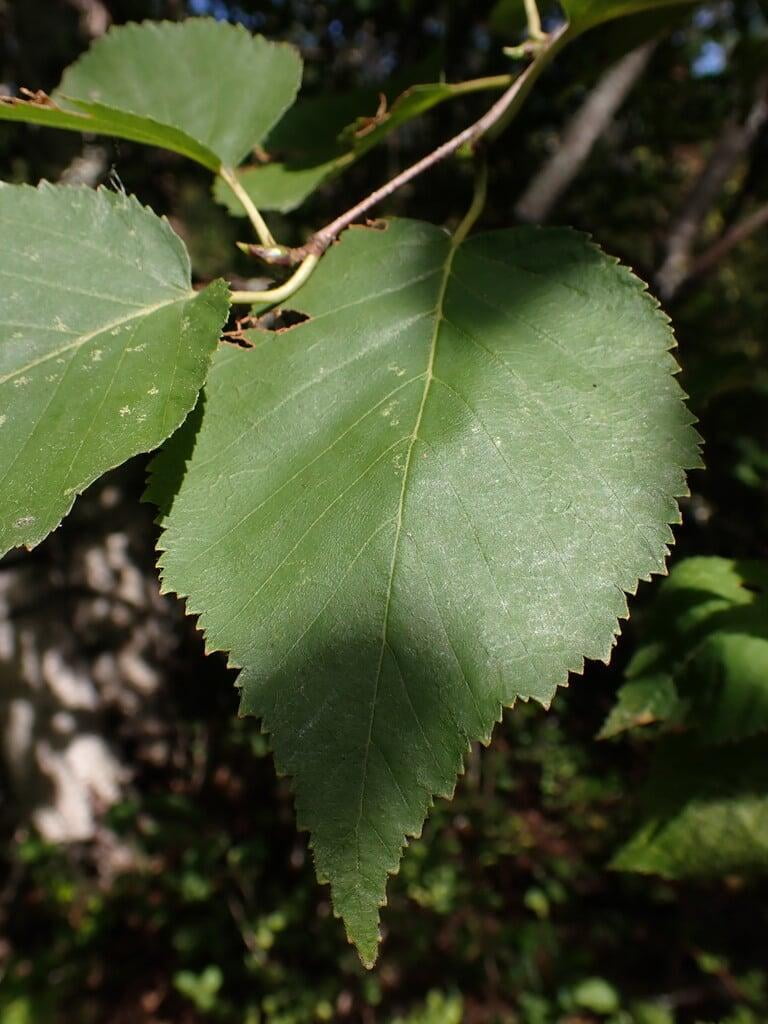
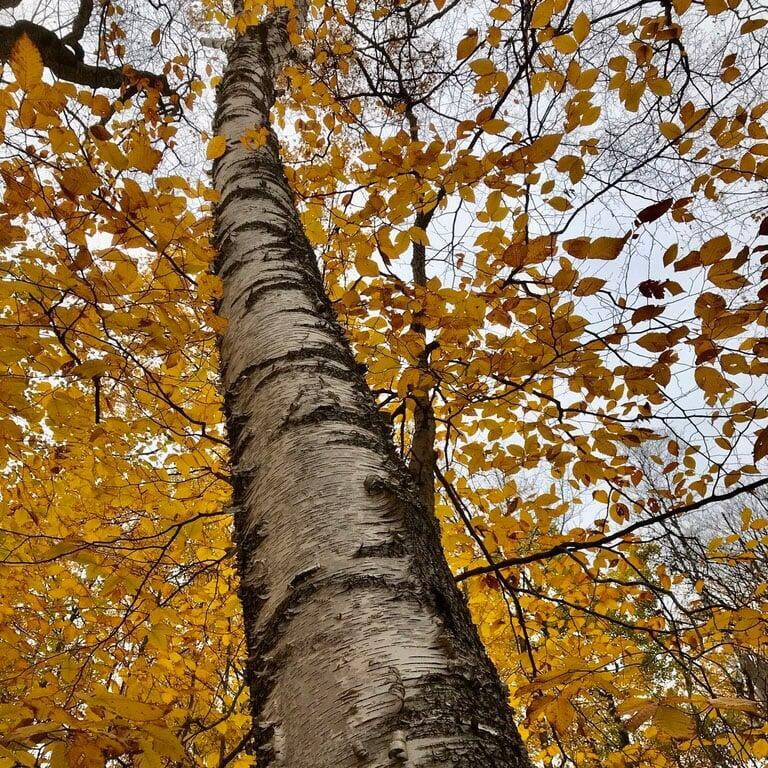
Betula papyrifera, commonly known as the paper birch, is a deciduous tree that belongs to the family Betulaceae. It is native to North America and is commonly found in cool and moist areas such as riverbanks, swamps, and wetlands. The paper birch is a medium-sized tree that can reach up to 90 feet in height and 30 inches in diameter. It has a slender trunk with thin, peeling, and white bark that can be easily distinguished from other tree species. The bark can also appear brownish-red or pinkish-orange when the tree is young. The leaves of the paper birch are oval-shaped, pointed at the tip, and have a serrated edge. They are bright green in color during the spring and summer, turning yellow in the fall. The tree produces male and female catkins that bloom in the spring, followed by small, winged seeds that are dispersed by the wind. The paper birch is a beautiful and popular ornamental tree, often used for landscaping and as a source of hardwood
Native Range:
Paper birch is found natively across the northern United States. From Washington and Oregon across to Maine and New York. It is found commonly across most parts of Minnesota.
Standard Plant Information:
Plant Height: 60-90'
Bloom time: April - May
Preferred Habitat: Does well in part shade to full sun. Generally found in upland forests.
Planting:
Planting a tree seedling or small potted tree properly is important to ensure its healthy growth and development. Here are the steps you can follow to plant a tree:
Choose the right spot: Select a spot with adequate sunlight, water, and soil drainage. Make sure the tree has enough space to grow to its full size without interfering with other plants, structures, or utility lines.
Prepare the soil: Dig a hole that is twice as wide and slightly shallower than the root ball of the seedling. Remove weeds or debris from the area. Loosen the soil around the edges of the hole to help the roots grow more easily.
Plant the seedling: Place the seedling in the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with the ground surface. Gently spread out the roots and fill in the hole with soil, tamping it down lightly as you go.
Water the seedling: Water the tree deeply and thoroughly after planting, making sure the soil is evenly moist. This will help settle the soil around the roots and eliminate any air pockets.
Monitor the growth: Keep an eye on the seedling to make sure it is getting enough water and sunlight, and that it is not being attacked by pests or diseases. Prune any damaged or dead branches as necessary, and provide support if needed.
By following these steps, you can help ensure the healthy growth and development of your newly planted tree seedling.

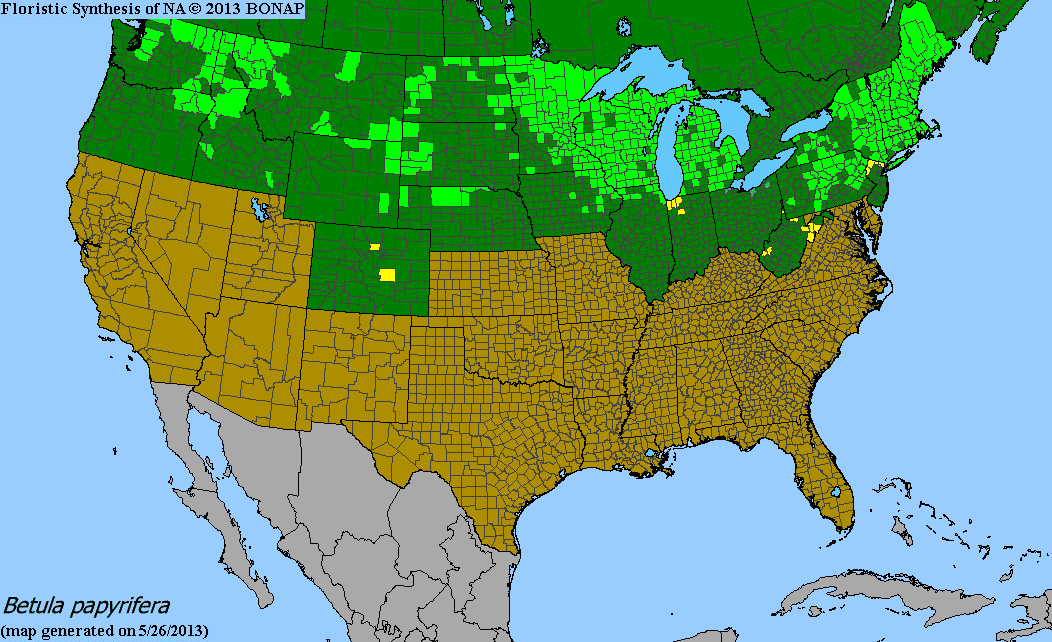
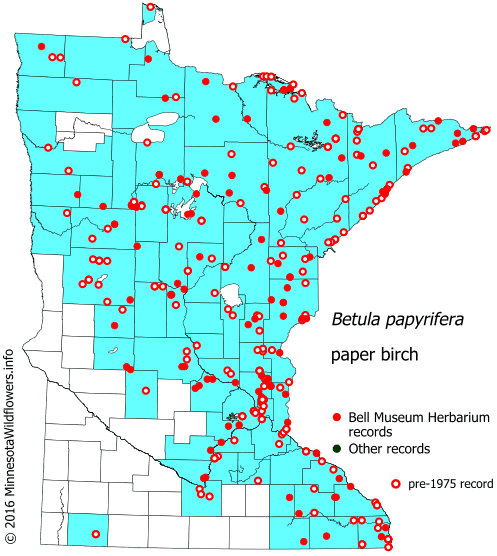
maps used with permission from MN Wildflowers
Betula papyrifera Gallery










