Solidago ptarmicoides
Upland goldenrod Description:
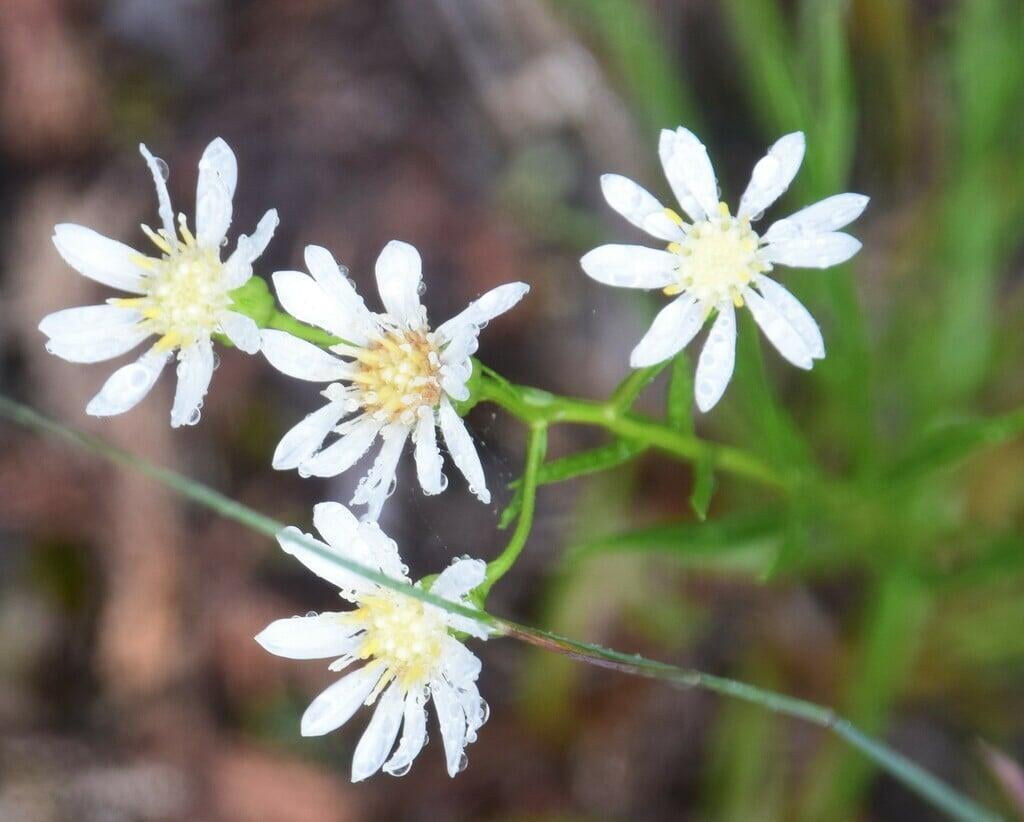
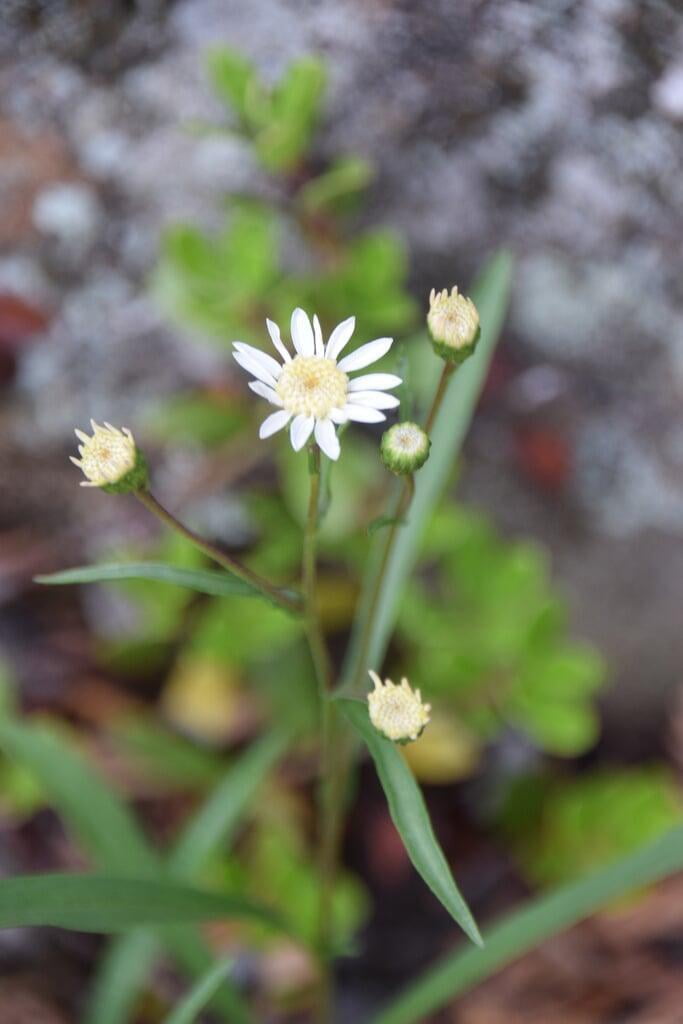
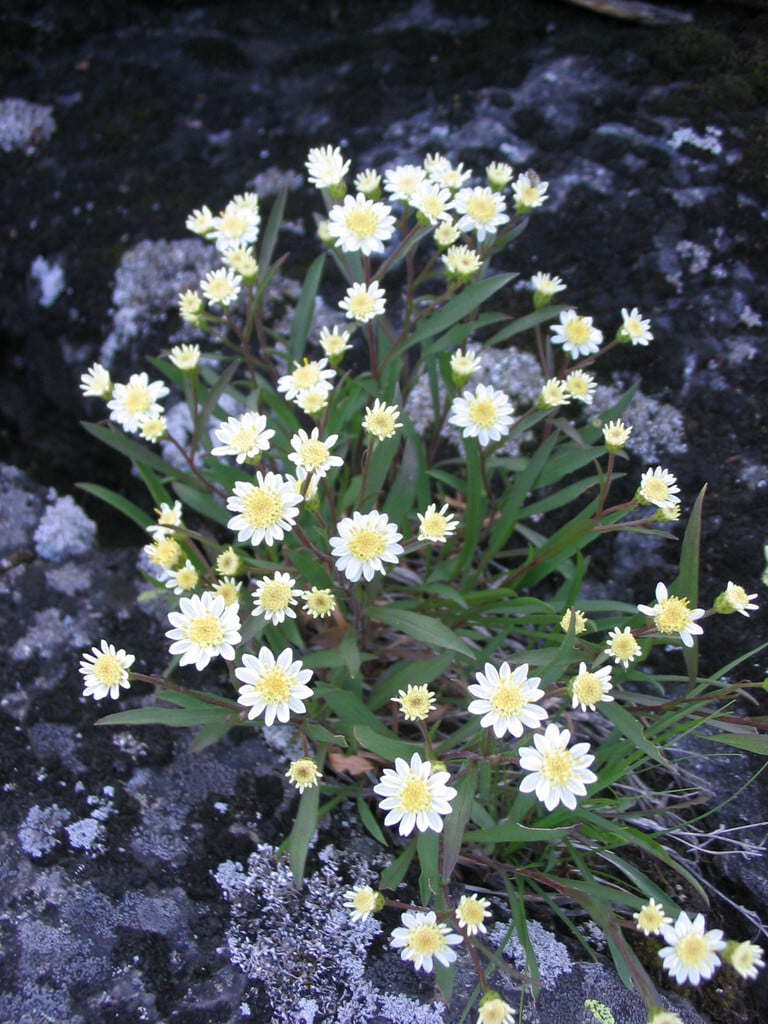
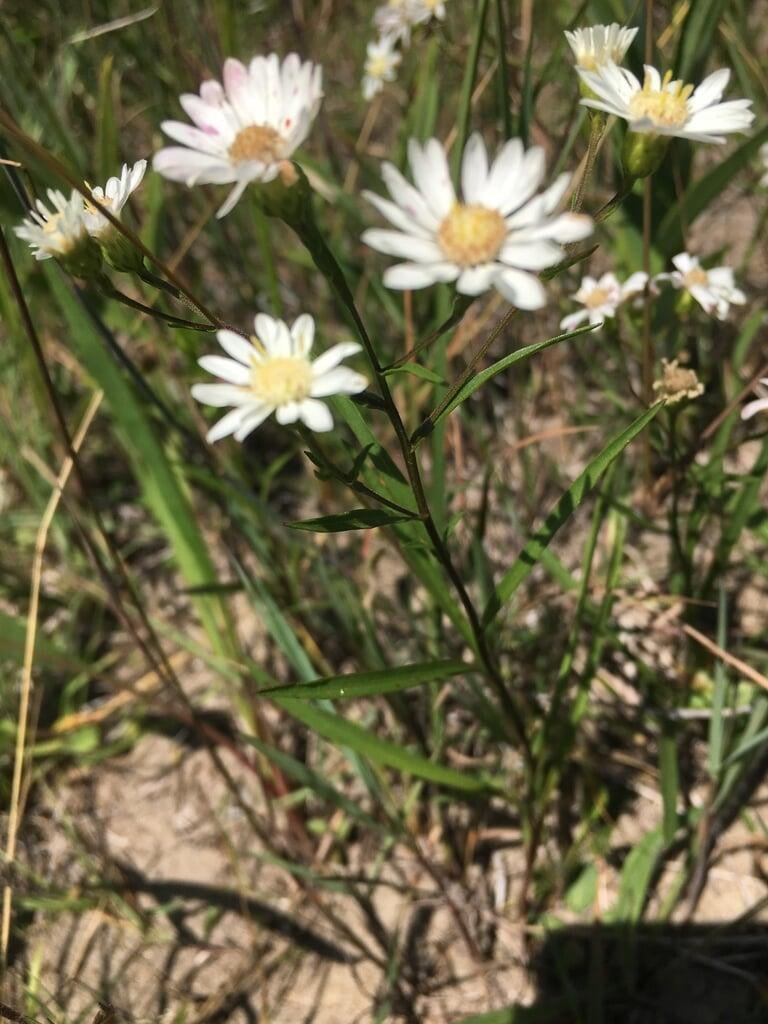
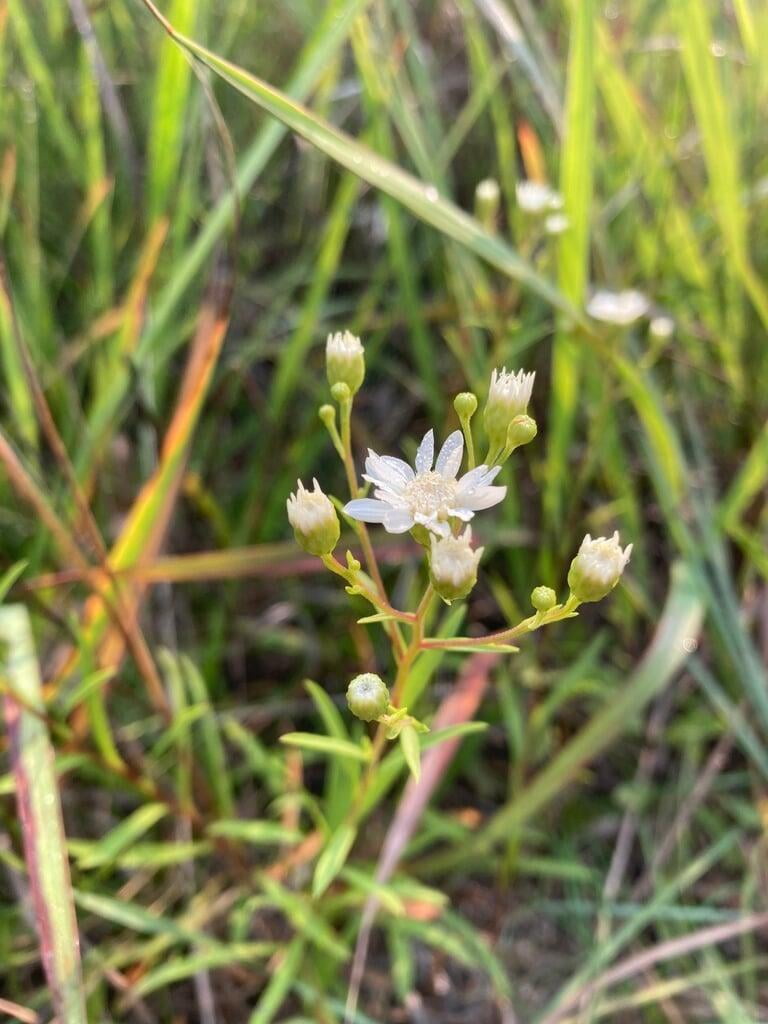
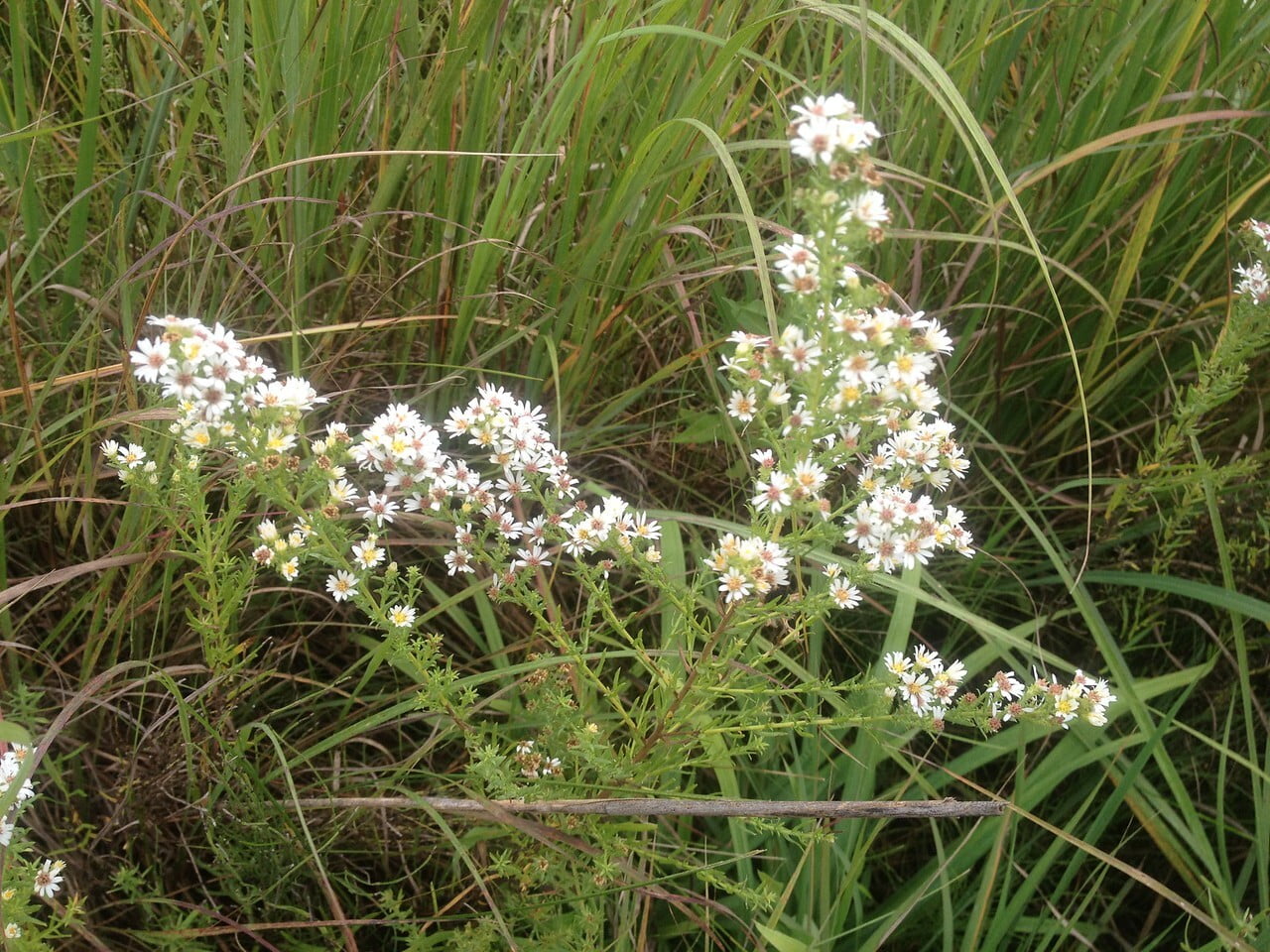
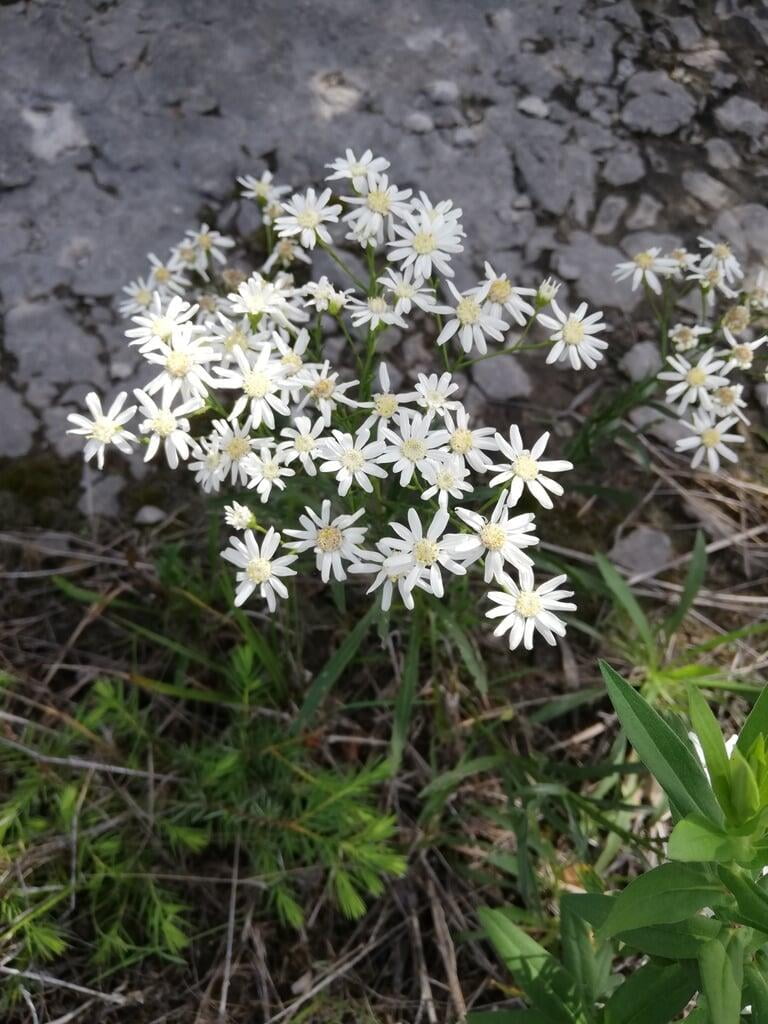
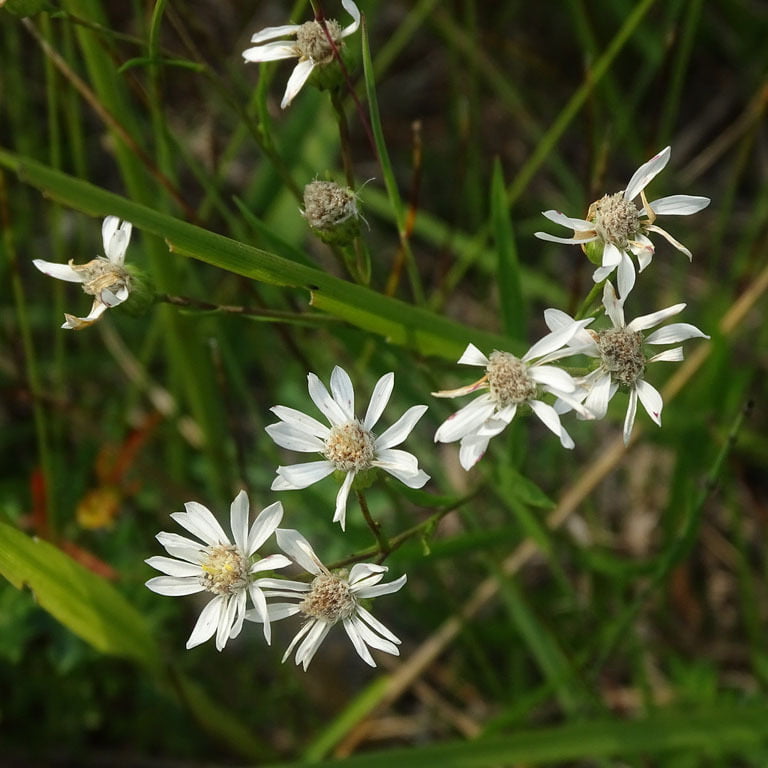
Solidago ptarmicoides, commonly known as bog goldenrod or prairie goldenrod, is a native North American wildflower species that belongs to the Asteraceae family. This perennial plant is known for its bright yellow flowers that bloom in late summer and early fall, adding a splash of color to gardens, prairies, and wetlands. Solidago ptarmicoides is a versatile plant that can grow in a variety of conditions, including moist and wet soils, making it an excellent addition to water gardens and other wetland areas. The plant also has a drought-tolerant nature, making it ideal for gardens in regions with low rainfall.
Apart from its ornamental value, Solidago ptarmicoides has ecological value, as it provides food and habitat for various species of wildlife, including bees, butterflies, and birds. The plant's nectar and pollen attract a wide range of pollinators, making it a vital species in pollinator conservation efforts. Additionally, the plant has been used for medicinal purposes by Native Americans, who used it to treat various ailments such as colds, fever, and diarrhea. The plant's roots and leaves are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, making it a valuable plant for traditional medicine. Overall, Solidago ptarmicoides is a valuable and versatile plant species that adds beauty, ecological value, and medicinal properties to wetland areas, water gardens, and other naturalized areas.
Native Range:
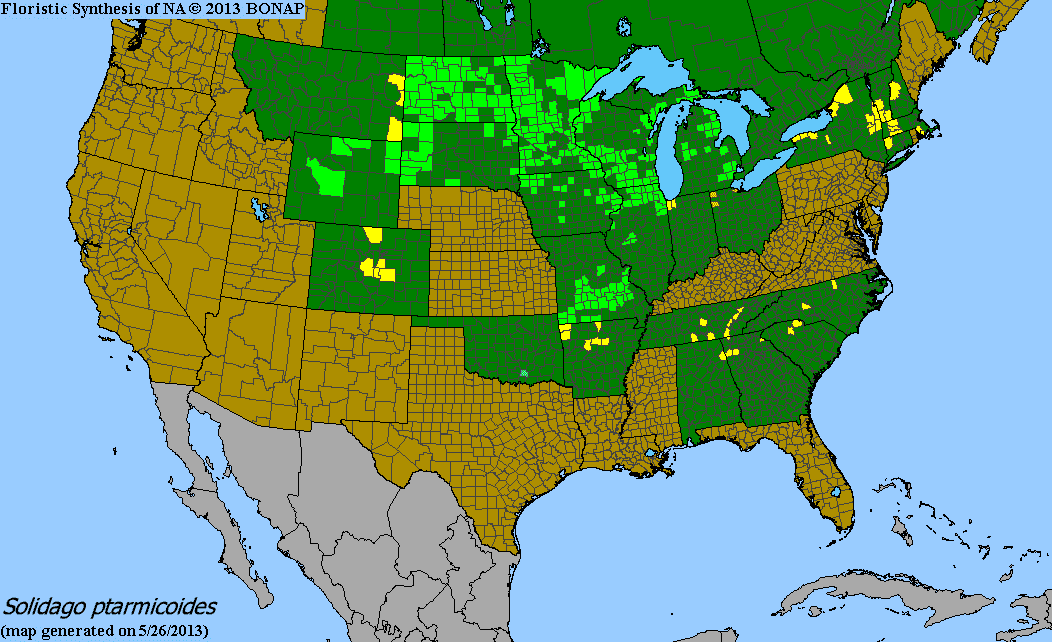
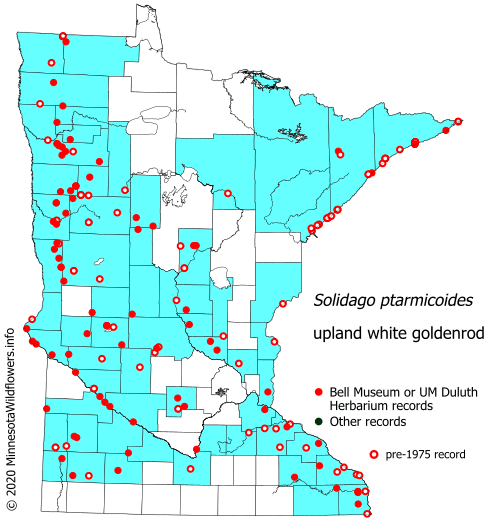
Upland goldenrod has a unique distribution in the United States. It is most common in the Midwest, but can be found as far west in Montana and as far south as Georgia. In Minnesota, Upland goldenrod is found across most of the state.
Standard Plant Information:
Plant Height: 1' - 2'
Bloom Time: July - September
Preferred Habitat: Does well in part shade to full sun in dry sandy or rocky soils. Often found in prairies, bluffs, rocky open woodland, and rocky outcrops.
Sowing:
For most homeowners, the best option is to scatter seed on the ground by hand broadcasting at a minimum of 16-64 pls ounces per acre. For even coverage, we recommend that you broadcast seed in perpendicular rows across the site to ensure even coverage.
You’ll want to broadcast any grass seed first, which will get raked into the soil lightly. Next, it is ideal to mulch the area lightly with either a clean (no seed) straw or preferably with our native Little Bluestem straw, sold at our retail garden centers. After a light mulching is complete, now it’s time to broadcast your native wildflower seeds, which should not be raked into the soil. A good rain or watering is sufficient to cover the seed.
Planting:
Simply dig a hole in the soil slightly larger than the plant’s roots. Ensure that the soil line of the plant is maintained during the transfer (i.e. the plant should be at the same level with the ground as it was in the pot). Pack any loose dirt back around the plant and make sure you water it well the same day to ensure it has the best chance of survival.