Eurybia macrophylla
Large-leaved aster Description:
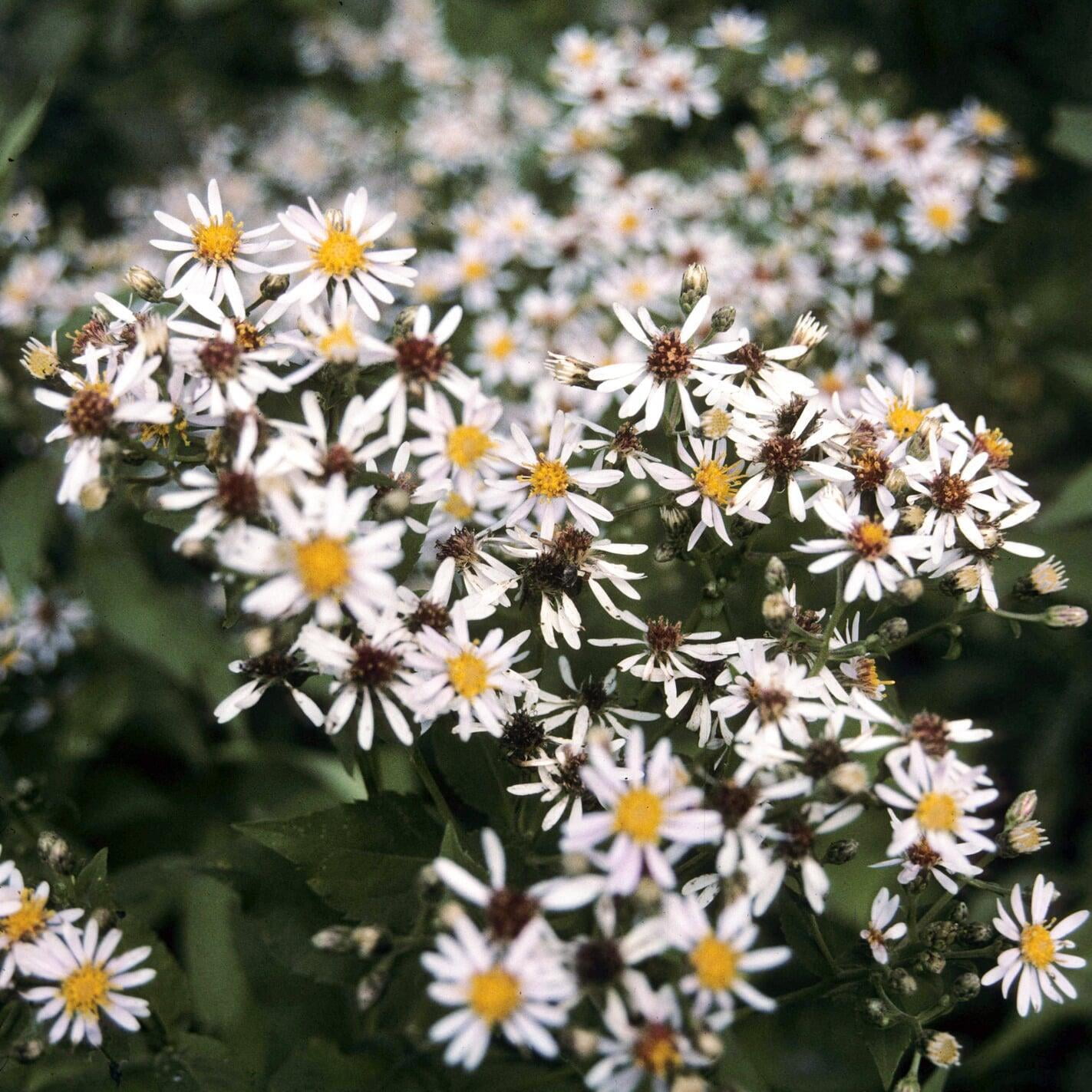
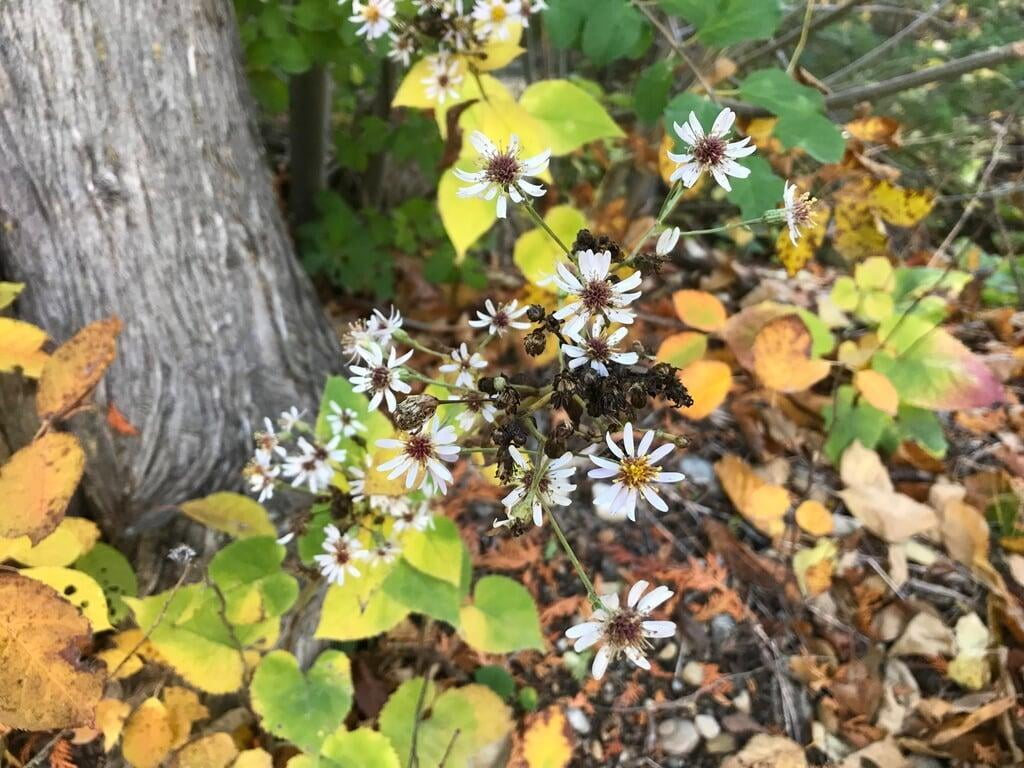
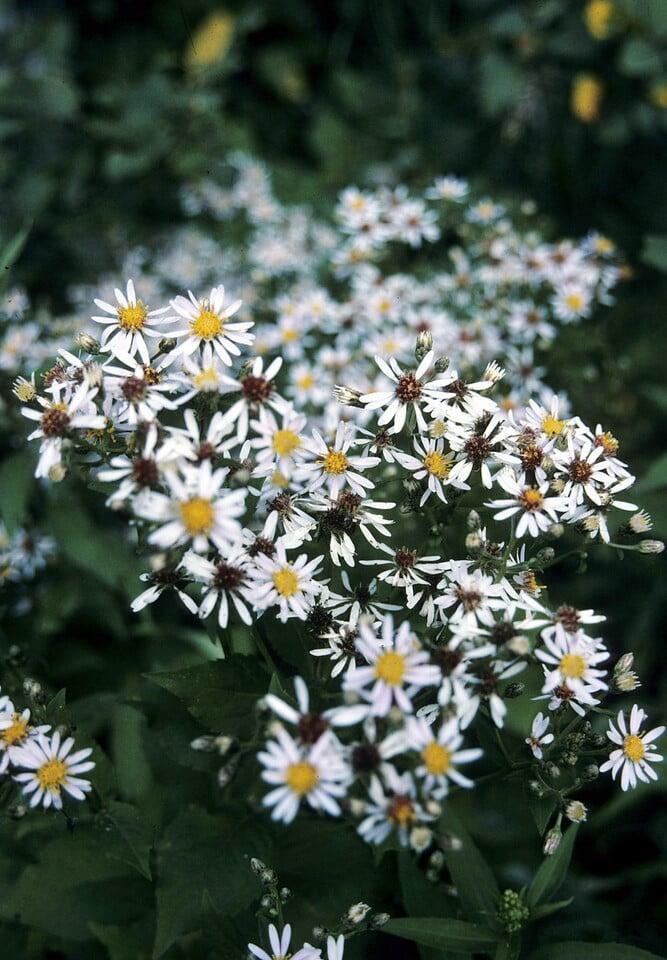
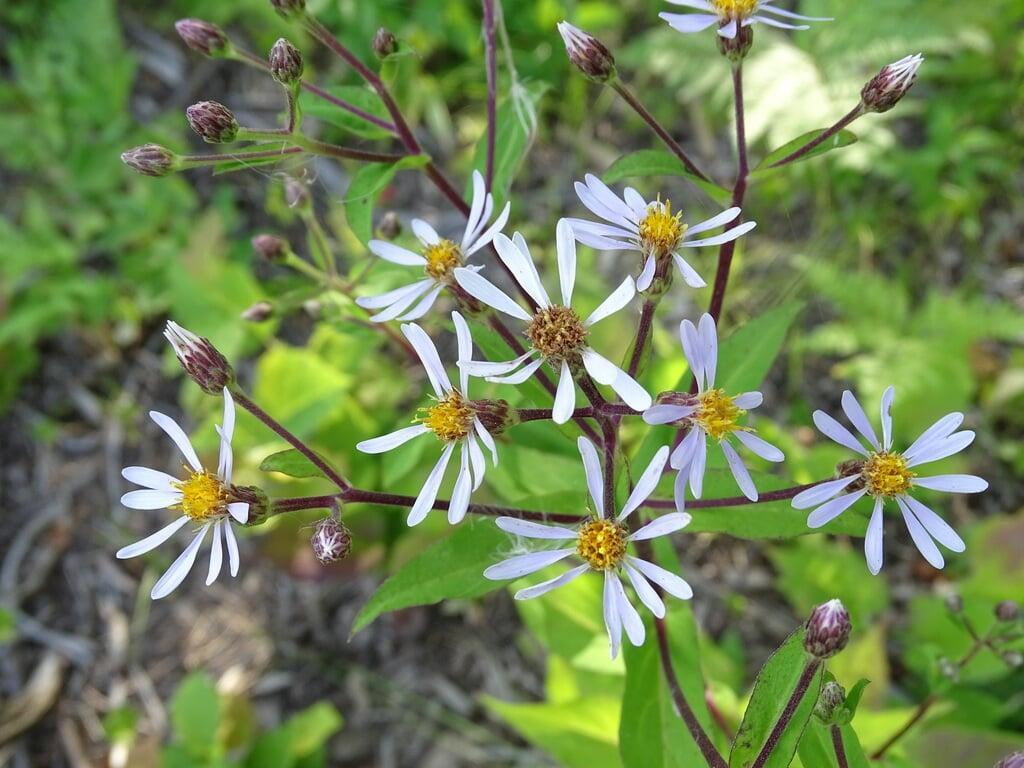
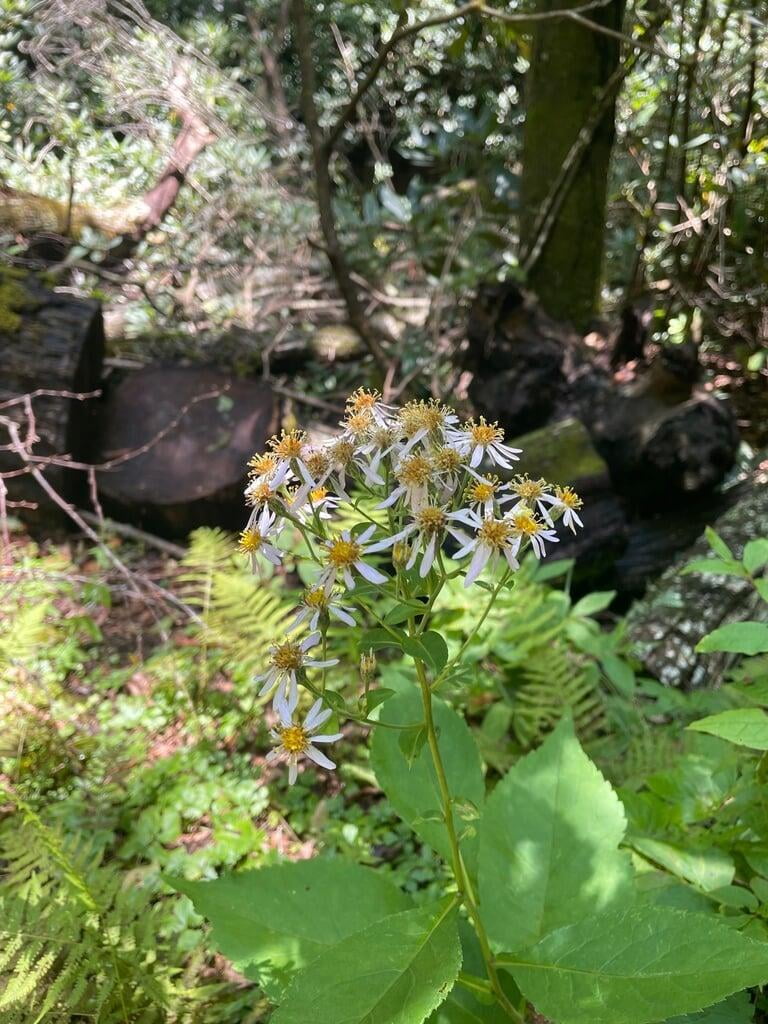
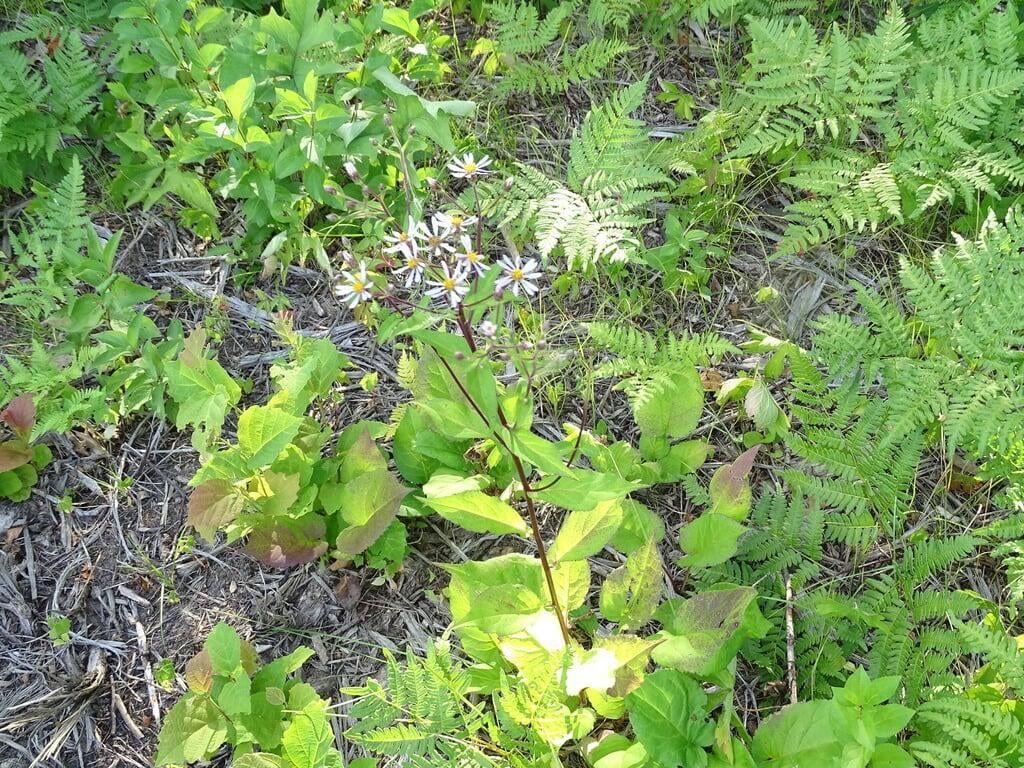
Eurybia macrophylla, also known as large-leaved aster, is a perennial wildflower native to eastern North America. It is commonly found in woodlands, shaded areas, and along streams and rivers. Large-leaved aster can grow up to 4 feet tall and has large, heart-shaped leaves that can measure up to 30 centimeters in length. The plant blooms in late summer to early fall, producing clusters of small, lavender to purple flowers that are attractive to a variety of pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and moths.
Eurybia macrophylla has a long history of use in traditional medicine by Native American tribes. The plant was used to treat a variety of ailments, including respiratory issues, digestive disorders, and skin conditions. It was also used as a general tonic to support the immune system.
Today, Eurybia macrophylla is still used in herbal medicine to support respiratory and digestive health and to strengthen the immune system. The plant contains a number of active compounds, including flavonoids and sesquiterpene lactones, that are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
Eurybia macrophylla is also valued for its ecological role. It is an important plant for pollinators, providing nectar and pollen for bees, butterflies, and other insects. The plant also provides important habitat for wildlife, and is an important component of woodland and streamside ecosystems. As a native plant, Eurybia macrophylla is also important for plant conservation efforts, helping to maintain biodiversity and preserve the natural heritage of North America.
Native Range:
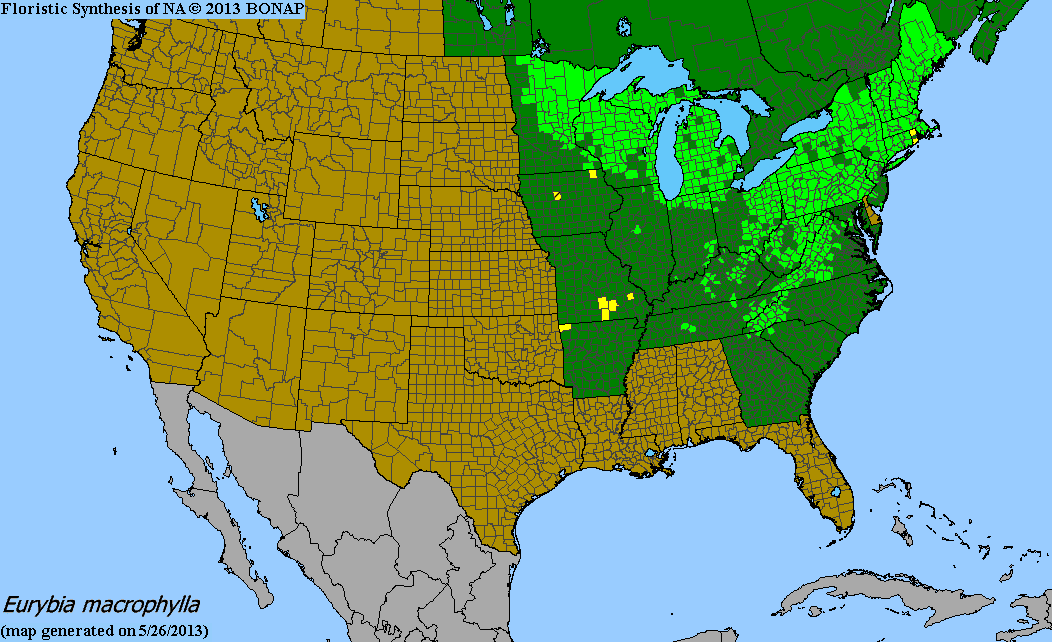
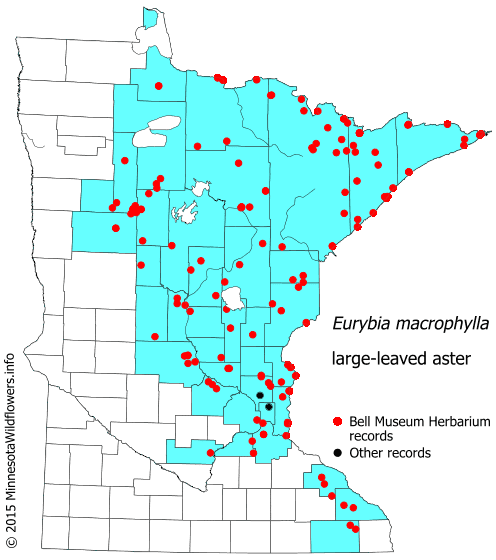
Large-leaved aster is found most commonly growing in the Upper Midwestern states including Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan as well as many of the Northeastern United States.
Standard Plant Information:
Plant Height: 1' - 4'
Bloom Time: July - October
Preferred Habitat: Does well in part shade to full shade. Often found in open woods and woodland edges.
Sowing:
For most homeowners, the best option is to scatter seed on the ground by hand broadcasting at a minimum of 16-64 pls ounces per acre. For even coverage, we recommend that you broadcast seed in perpendicular rows across the site to ensure even coverage.
You’ll want to broadcast any grass seed first, which will get raked into the soil lightly. Next, it is ideal to mulch the area lightly with either a clean (no seed) straw or preferably with our native Little Bluestem straw, sold at our retail garden centers. After a light mulching is complete, now it’s time to broadcast your native wildflower seeds, which should not be raked into the soil. A good rain or watering is sufficient to cover the seed.
Planting:
Simply dig a hole in the soil slightly larger than the plant’s roots. Ensure that the soil line of the plant is maintained during the transfer (i.e. the plant should be at the same level with the ground as it was in the pot). Pack any loose dirt back around the plant and make sure you water it well the same day to ensure it has the best chance of survival.